It is sometimes referred to as the bicipital groove. humerus, An official website of the United States government. Immediately adjacent to the head is the narrower anatomical neck, which allows for a wider range of movements of the head within the shoulder joint. The bone forming the upper arm is the humerus. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. As its name indicates, it is the site of attachment for the deltoid muscle. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. In elbow extension, the tip of the ulnar olecranon process lodges into this fossa. Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD, PhD In these, the olecranon of the ulna is driven upward, resulting in a fracture across the distal humerus, above both epicondyles (supracondylar fracture), or a fracture between the epicondyles, thus separating one or both of the epicondyles from the body of the humerus (intercondylar fracture). Read more. An interphalangeal joint is one of the articulations between adjacent phalanges of the digits (see (Figure)). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. trochlea.

The axillary nerve and circumflex humeral vessels lie against the bone here. These are arranged into proximal and distal rows of four bones each. The correlation between acromion-axillary nerve distance and upper arm length; a cadaveric study. What are the three arches of the hand, and what is the importance of these during the gripping of an object? It articulates with the cupshaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone. The carpal bones, together with the flexor retinaculum, also form the carpal tunnel of the wrist. The humerus articulates with thescapulaproximally at theglenohumeral jointso it participates in the movements of the shoulder.
The lateral border begins just distal to the greater tubercle of the humerus. Inferior to this point on the medial side is the radial tuberosity, an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point.
The remaining metacarpal bones are united together to form the palm of the hand. In birds, where forelimb anatomy has an adaptation for flight, its functional if not[1] ontogenetic equivalent is the dorsal condyle of the humerus. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. In: StatPearls [Internet]. It articulates with the radius and ulna bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. Several muscles of the forearm responsible for extension at the wrist attach to the humerus immediately above the capitulum and trochlea. The distal radioulnar joint is found between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius.

and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones Due to our constant use of the hands and the rest of our upper limbs, an injury to any of these areas will cause a significant loss of functional ability. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. anterior, Projecting from the posterior side of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna, a short bony projection. -, Hamilton MA, Diep P, Roche C, Flurin PH, Wright TW, Zuckerman JD, Routman H. Effect of reverse shoulder design philosophy on muscle moment arms. The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas, which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. The paper about Bacho Ki Paleoanthropology, genetics, and evolution, Louis Leakey on the failure of the stage model of human evolution, Ancient genetic introgression between cave hyenas and spotted hyenas, Brain-body allometry revisited across mammals, Fossil profile: Zlat k and the Neandertal heritage of early Upper Paleolithic Europeans. Salvage of upper extremities with humeral fracture and associated brachial artery injury. The bone of the upper arm is called the humerus. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Would you like email updates of new search results? Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Head, anatomical neck, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, Impact, avulsion, transverse, spiral, intercondylar. The Gartland classification is used for these fractures: Type 1 can usually be managed conservatively with an above elbow cast whereas types 2 and 3 typically require surgical fixation with crossed, bi-cortical k-wires. You will find the distal end of the bone very helpful, with the trochlea medial and capitulum lateral, and the olecranon fossa on the posterior aspect. How well do you know the other 205 bones in the body? The pull of the deltoid muscle causes the proximal fragment to displace laterally. The smaller lesser tubercle of the humerus is found on the anterior aspect of the humerus. Itarticulates with both the ulna and radius and consists of a medial trochlea and a lateral capitulum, which are separated by a faint groove. This is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm, a sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the ulna and radius bones. It is most commonly seen in the middle-aged and in the elderly. Just below this on the anterior ulna is a roughened area called the ulnar tuberosity. The most commonly fractured carpal bone is the scaphoid, often resulting from a fall onto the hand. Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus ((Figure)). These will pass the force through the elbow joint into the humerus of the arm, and then through the glenohumeral joint into the scapula. Your friend runs out of gas and you have to help push his car. On the lateral side, a bump called the greater tubercle projects proximally. The metacarpal bones are numbered 15, starting with the thumb side. The coronoid fossa is a smaller hollow that is also located superior to the trochlea, but on the anterior surface. As you push against the car, forces will pass from the metacarpal bones of your hand into the carpal bones at the base of your hand. and transmitted securely. [Kocher approach to the elbow and its options]. The superficial muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm originate from the anterior surface of the medial epicondyle. This region contains two bones, the ulna medially and the radius on the lateral (thumb) side. The medial border is similar to the lateral border in that it forms the medial supracondylar ridge distally. How many bones are there in the upper limbs combined? The greater tubercle is the most lateral portion of the proximal end of the humerus. The radial nerve innervates the extensors of the wrist. Charlotte O'Leary BSc, MBChB It only has an anterior surface. An easy way to remember the relation of latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major and teres major muscles as they insert in the intertubercular sulcus is to use the following mnemonic! The ulna is located on the medial side of the forearm, and the radius is on the lateral side. These consist of the arm, located between the shoulder and elbow joints; the forearm, which is between the elbow and wrist joints; and the hand, which is located distal to the wrist. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the humerus joins with the shaft, can result in an impacted fracture, in which the distal portion of the humerus is driven into the proximal portion. A Colles fracture of the distal radius is the most common forearm fracture. lateral, Immediately lateral to the trochlea is the capitulum (small head), a knob-like structure located on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The head is a hemispheroidal shape, withhyaline cartilage coveringits smooth articular surface. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. The forearm is the region of the upper limb located between the elbow and wrist joints. Pectoralis major, teres major andlatissimus dorsi insert on the lips of the intertubercular sulcus. This injury results in a characteristic dinner fork bend of the forearm just above the wrist due to the posterior displacement of the hand. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. The lateral side of the shaft forms a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna. When the elbow is in the extended position, the posterior and inferior aspects of the trochlea are in contact with the ulna.
Eur J Radiol. In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. Watch this video to see how fractures of the distal radius bone can affect the wrist joint. 7.6A: Humerus (The Upper Arm) is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Test your knowledge with our bone quizzes and labeled diagrams. Thegreater tuberosityis located laterally on the humerus and has anterior and posterior surfaces. Lateral to the trochlea is thecapitulum,which articulates with the radius. The medially located trochlea articulates with the ulna. The other, called the capitulum, is a small spherical structure lateral to the trochlea that articulates with the head of the radius. This is the large, round, smooth region that faces medially.
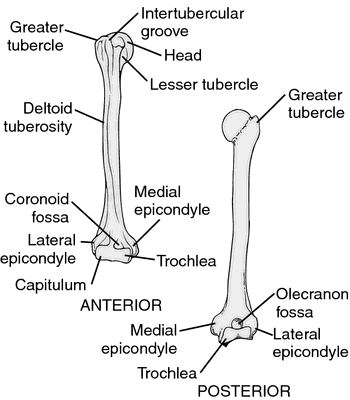
The lateral aspect also contains multiple vascular foramina. The capitulum is a convex and rounded projection that covers the anterior and inferior surfaces of the lateral condyle of the humerus. Surgery can return the joint surface to its original smoothness, thus allowing for the return of normal function. On the posterior surface of the condyle is the olecranon fossa, which articulates with the olecranon of the ulnar bone upon flexion of the elbow joint. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the humerus - its bony landmarks and clinical correlations. Cross section views reveal it to be circular proximally and flattened distally. The medial epicondyle is a blunt projection superomedial to the medial condyle, which forms at the end of the medial border of the humerus. Both the greater and lesser tubercles serve as attachment sites for muscles that act across the shoulder joint. 2014 Aug;97 Suppl 8:S27-33. Ive been writing about ancient mixture between species for a long time now. The anterior interosseous nerve can be tested by asking the patient to make an okay sign, testing for weakness of flexor pollicis longus. The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the hand. It provides attachment for the last rotator cuff muscle - the subscapularis. The five metacarpal bones form the palm of the hand. The key neurovascular structures at risk here are the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex artery. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions. The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. Immediately distal to the supraepicondylar ridges areextracapsular projections of bone, the lateral andmedial epicondyles. If compression occurs, the resulting ischemia (lack of oxygen) due to reduced blood flow can quickly produce irreparable damage to the forearm muscles. Romer (1976) homologizes the capitellum in Archosauromorphs with the groove separating the medial and lateral condyles. It only has an anterior surface. Deep dissection. The radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm (see (Figure)). The trochlea has a surface shaped like a pulley and covers the anterior, posterior and inferior surfaces of the medial condyle of the humerus. The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones contribute to the formation of the radiocarpal joint. This allows it a freedom of motion that is independent of the other metacarpal bones, which is very important for thumb mobility. humeral head, The distal ends of the metacarpal bones articulate with the proximal phalanx bones of the thumb and fingers. The margin of the smooth area of the head is the anatomical neck of the humerus. The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm. The thumb contains a proximal and a distal phalanx, whereas the remaining digits each contain proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. This results in unopposed flexion of the wrist, known as wrist drop. The shaft of the humerus is the site of attachment for various muscles. An intertubercular groove appears proximally, which demarcates the two tubercles vertically.
condyle humeral limb thoracic bones quizlet insertion This area contains the humerus. Bookshelf In addition, four major nerves for shoulder and upper limb muscles are closely associated with different regions of the humerus, and thus, humeral fractures may also damage these nerves. In the articulated hand, the carpal bones form a U-shaped grouping. The anatomical neck of the humerus is the residual epiphyseal plate. The following musclesattach to the humerus along its shaft: A mid-shaft fracture of the humerus risk damage to theradial nerve and profunda brachii artery (as they are tightly bound in the radial groove). Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site. Unlike the trochlea, it doesnt cover the posterior surface. Reading time: 13 minutes. The carrying angle is larger in females to accommodate their wider pelvis. Please use the, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance. This faces medially, upwards and backwards and is separated from the greater and lesser tuberosities by the anatomical neck. Both can be palpated at the elbow. This serves as an attachment point for a connective tissue structure that unites the distal ends of the ulna and radius. Legal. The deltoid muscle covers the lateral aspect of the greater tubercle, resulting in the normal rounded shape of the shoulder. -, Prescher A. Anatomical basics, variations, and degenerative changes of the shoulder joint and shoulder girdle. This involves a complete transverse fracture across the distal radius that drives the separated distal fragment of the radius posteriorly and superiorly. Due to the poor blood supply to the scaphoid bone, healing will be slow and there is the danger of bone necrosis and subsequent degenerative joint disease of the wrist. This results in separation of one or both of the condyles from the shaft of the humerus. The eight carpal bones form the base of the hand. These include the: The olecranon fossa is a deep hollowed area on the posterior surface, superior to the trochlea. The deltoid, corocobrachialis, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles attach to the anterior surface, with the triceps brachii attaching to the posterior. The most proximal portion of the humerus is the head of the humerus, which forms a ball and socket joint with the glenoid cavity on the scapula. The more medial of these areas is the trochlea, a spindle- or pulley-shaped region (trochlea = pulley), which articulates with the ulna bone. Romer, A.S. 1976 Osteology of the reptiles. Thus, it starts and finishes on the lateral side. The proximal and distal rows of carpal bones articulate with each other to form the midcarpal joint (see (Figure)). Fig 4 Bony landmarks of the distal humerus. The proximal humerus is marked by a head, anatomical neck, surgical neck, greater and lesser tuberosity and intertubercular sulcus. The proximal end of the humerus is dominated by a half-spherical articular surface, called the head, that forms the ball of the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. It articulates with the radius and ulna to form the elbow joint. It is more common in children than adults. Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Identify the divisions of the upper limb and describe the bones in each region, List the bones and bony landmarks that articulate at each joint of the upper limb, is found on the medial side of the forearm, has a head that articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, does not articulate with any of the carpal bones, has the radial tuberosity located near its distal end. The anterolateral surfaceis an area limited between the anterior and lateral borders. Here's an easy way to help you remember them! These spaces accommodate the forearm bones when the elbow is fully bent (flexed). The digits are also numbered 15, with the thumb being number 1. A direct blow to the arm can result in a transverse fracture of the humeral shaft. Between the two tubercles lies a deep grove called the intertubercular sulcus, through which the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii runs. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! Fig 3 Wristdrop of the left forearm, as a result of radial nerve palsy. By Anatomography [CC BY-SA 2.1 jp], via Wikimedia Commons, [caption id="attachment_8000" align="aligncenter" width="208"], [caption id="attachment_21152" align="aligncenter" width="871"], [caption id="attachment_10467" align="aligncenter" width="278"], [caption id="attachment_119738" align="aligncenter" width="658"], [caption id="attachment_3599" align="aligncenter" width="336"].
 The axillary nerve and circumflex humeral vessels lie against the bone here. These are arranged into proximal and distal rows of four bones each. The correlation between acromion-axillary nerve distance and upper arm length; a cadaveric study. What are the three arches of the hand, and what is the importance of these during the gripping of an object? It articulates with the cupshaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone. The carpal bones, together with the flexor retinaculum, also form the carpal tunnel of the wrist. The humerus articulates with thescapulaproximally at theglenohumeral jointso it participates in the movements of the shoulder. The lateral border begins just distal to the greater tubercle of the humerus. Inferior to this point on the medial side is the radial tuberosity, an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point. The remaining metacarpal bones are united together to form the palm of the hand. In birds, where forelimb anatomy has an adaptation for flight, its functional if not[1] ontogenetic equivalent is the dorsal condyle of the humerus. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. In: StatPearls [Internet]. It articulates with the radius and ulna bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. Several muscles of the forearm responsible for extension at the wrist attach to the humerus immediately above the capitulum and trochlea. The distal radioulnar joint is found between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius.
The axillary nerve and circumflex humeral vessels lie against the bone here. These are arranged into proximal and distal rows of four bones each. The correlation between acromion-axillary nerve distance and upper arm length; a cadaveric study. What are the three arches of the hand, and what is the importance of these during the gripping of an object? It articulates with the cupshaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone. The carpal bones, together with the flexor retinaculum, also form the carpal tunnel of the wrist. The humerus articulates with thescapulaproximally at theglenohumeral jointso it participates in the movements of the shoulder. The lateral border begins just distal to the greater tubercle of the humerus. Inferior to this point on the medial side is the radial tuberosity, an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point. The remaining metacarpal bones are united together to form the palm of the hand. In birds, where forelimb anatomy has an adaptation for flight, its functional if not[1] ontogenetic equivalent is the dorsal condyle of the humerus. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. In: StatPearls [Internet]. It articulates with the radius and ulna bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. Several muscles of the forearm responsible for extension at the wrist attach to the humerus immediately above the capitulum and trochlea. The distal radioulnar joint is found between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius.  and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones Due to our constant use of the hands and the rest of our upper limbs, an injury to any of these areas will cause a significant loss of functional ability. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. anterior, Projecting from the posterior side of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna, a short bony projection. -, Hamilton MA, Diep P, Roche C, Flurin PH, Wright TW, Zuckerman JD, Routman H. Effect of reverse shoulder design philosophy on muscle moment arms. The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas, which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. The paper about Bacho Ki Paleoanthropology, genetics, and evolution, Louis Leakey on the failure of the stage model of human evolution, Ancient genetic introgression between cave hyenas and spotted hyenas, Brain-body allometry revisited across mammals, Fossil profile: Zlat k and the Neandertal heritage of early Upper Paleolithic Europeans. Salvage of upper extremities with humeral fracture and associated brachial artery injury. The bone of the upper arm is called the humerus. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Would you like email updates of new search results? Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Head, anatomical neck, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, Impact, avulsion, transverse, spiral, intercondylar. The Gartland classification is used for these fractures: Type 1 can usually be managed conservatively with an above elbow cast whereas types 2 and 3 typically require surgical fixation with crossed, bi-cortical k-wires. You will find the distal end of the bone very helpful, with the trochlea medial and capitulum lateral, and the olecranon fossa on the posterior aspect. How well do you know the other 205 bones in the body? The pull of the deltoid muscle causes the proximal fragment to displace laterally. The smaller lesser tubercle of the humerus is found on the anterior aspect of the humerus. Itarticulates with both the ulna and radius and consists of a medial trochlea and a lateral capitulum, which are separated by a faint groove. This is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm, a sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the ulna and radius bones. It is most commonly seen in the middle-aged and in the elderly. Just below this on the anterior ulna is a roughened area called the ulnar tuberosity. The most commonly fractured carpal bone is the scaphoid, often resulting from a fall onto the hand. Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus ((Figure)). These will pass the force through the elbow joint into the humerus of the arm, and then through the glenohumeral joint into the scapula. Your friend runs out of gas and you have to help push his car. On the lateral side, a bump called the greater tubercle projects proximally. The metacarpal bones are numbered 15, starting with the thumb side. The coronoid fossa is a smaller hollow that is also located superior to the trochlea, but on the anterior surface. As you push against the car, forces will pass from the metacarpal bones of your hand into the carpal bones at the base of your hand. and transmitted securely. [Kocher approach to the elbow and its options]. The superficial muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm originate from the anterior surface of the medial epicondyle. This region contains two bones, the ulna medially and the radius on the lateral (thumb) side. The medial border is similar to the lateral border in that it forms the medial supracondylar ridge distally. How many bones are there in the upper limbs combined? The greater tubercle is the most lateral portion of the proximal end of the humerus. The radial nerve innervates the extensors of the wrist. Charlotte O'Leary BSc, MBChB It only has an anterior surface. An easy way to remember the relation of latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major and teres major muscles as they insert in the intertubercular sulcus is to use the following mnemonic! The ulna is located on the medial side of the forearm, and the radius is on the lateral side. These consist of the arm, located between the shoulder and elbow joints; the forearm, which is between the elbow and wrist joints; and the hand, which is located distal to the wrist. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the humerus joins with the shaft, can result in an impacted fracture, in which the distal portion of the humerus is driven into the proximal portion. A Colles fracture of the distal radius is the most common forearm fracture. lateral, Immediately lateral to the trochlea is the capitulum (small head), a knob-like structure located on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The head is a hemispheroidal shape, withhyaline cartilage coveringits smooth articular surface. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. The forearm is the region of the upper limb located between the elbow and wrist joints. Pectoralis major, teres major andlatissimus dorsi insert on the lips of the intertubercular sulcus. This injury results in a characteristic dinner fork bend of the forearm just above the wrist due to the posterior displacement of the hand. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. The lateral side of the shaft forms a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna. When the elbow is in the extended position, the posterior and inferior aspects of the trochlea are in contact with the ulna. Eur J Radiol. In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. Watch this video to see how fractures of the distal radius bone can affect the wrist joint. 7.6A: Humerus (The Upper Arm) is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Test your knowledge with our bone quizzes and labeled diagrams. Thegreater tuberosityis located laterally on the humerus and has anterior and posterior surfaces. Lateral to the trochlea is thecapitulum,which articulates with the radius. The medially located trochlea articulates with the ulna. The other, called the capitulum, is a small spherical structure lateral to the trochlea that articulates with the head of the radius. This is the large, round, smooth region that faces medially.
and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones Due to our constant use of the hands and the rest of our upper limbs, an injury to any of these areas will cause a significant loss of functional ability. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. anterior, Projecting from the posterior side of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna, a short bony projection. -, Hamilton MA, Diep P, Roche C, Flurin PH, Wright TW, Zuckerman JD, Routman H. Effect of reverse shoulder design philosophy on muscle moment arms. The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas, which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. The paper about Bacho Ki Paleoanthropology, genetics, and evolution, Louis Leakey on the failure of the stage model of human evolution, Ancient genetic introgression between cave hyenas and spotted hyenas, Brain-body allometry revisited across mammals, Fossil profile: Zlat k and the Neandertal heritage of early Upper Paleolithic Europeans. Salvage of upper extremities with humeral fracture and associated brachial artery injury. The bone of the upper arm is called the humerus. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Would you like email updates of new search results? Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Head, anatomical neck, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, Impact, avulsion, transverse, spiral, intercondylar. The Gartland classification is used for these fractures: Type 1 can usually be managed conservatively with an above elbow cast whereas types 2 and 3 typically require surgical fixation with crossed, bi-cortical k-wires. You will find the distal end of the bone very helpful, with the trochlea medial and capitulum lateral, and the olecranon fossa on the posterior aspect. How well do you know the other 205 bones in the body? The pull of the deltoid muscle causes the proximal fragment to displace laterally. The smaller lesser tubercle of the humerus is found on the anterior aspect of the humerus. Itarticulates with both the ulna and radius and consists of a medial trochlea and a lateral capitulum, which are separated by a faint groove. This is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm, a sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the ulna and radius bones. It is most commonly seen in the middle-aged and in the elderly. Just below this on the anterior ulna is a roughened area called the ulnar tuberosity. The most commonly fractured carpal bone is the scaphoid, often resulting from a fall onto the hand. Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus ((Figure)). These will pass the force through the elbow joint into the humerus of the arm, and then through the glenohumeral joint into the scapula. Your friend runs out of gas and you have to help push his car. On the lateral side, a bump called the greater tubercle projects proximally. The metacarpal bones are numbered 15, starting with the thumb side. The coronoid fossa is a smaller hollow that is also located superior to the trochlea, but on the anterior surface. As you push against the car, forces will pass from the metacarpal bones of your hand into the carpal bones at the base of your hand. and transmitted securely. [Kocher approach to the elbow and its options]. The superficial muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm originate from the anterior surface of the medial epicondyle. This region contains two bones, the ulna medially and the radius on the lateral (thumb) side. The medial border is similar to the lateral border in that it forms the medial supracondylar ridge distally. How many bones are there in the upper limbs combined? The greater tubercle is the most lateral portion of the proximal end of the humerus. The radial nerve innervates the extensors of the wrist. Charlotte O'Leary BSc, MBChB It only has an anterior surface. An easy way to remember the relation of latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major and teres major muscles as they insert in the intertubercular sulcus is to use the following mnemonic! The ulna is located on the medial side of the forearm, and the radius is on the lateral side. These consist of the arm, located between the shoulder and elbow joints; the forearm, which is between the elbow and wrist joints; and the hand, which is located distal to the wrist. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the humerus joins with the shaft, can result in an impacted fracture, in which the distal portion of the humerus is driven into the proximal portion. A Colles fracture of the distal radius is the most common forearm fracture. lateral, Immediately lateral to the trochlea is the capitulum (small head), a knob-like structure located on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The head is a hemispheroidal shape, withhyaline cartilage coveringits smooth articular surface. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. The forearm is the region of the upper limb located between the elbow and wrist joints. Pectoralis major, teres major andlatissimus dorsi insert on the lips of the intertubercular sulcus. This injury results in a characteristic dinner fork bend of the forearm just above the wrist due to the posterior displacement of the hand. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. The lateral side of the shaft forms a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna. When the elbow is in the extended position, the posterior and inferior aspects of the trochlea are in contact with the ulna. Eur J Radiol. In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. Watch this video to see how fractures of the distal radius bone can affect the wrist joint. 7.6A: Humerus (The Upper Arm) is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Test your knowledge with our bone quizzes and labeled diagrams. Thegreater tuberosityis located laterally on the humerus and has anterior and posterior surfaces. Lateral to the trochlea is thecapitulum,which articulates with the radius. The medially located trochlea articulates with the ulna. The other, called the capitulum, is a small spherical structure lateral to the trochlea that articulates with the head of the radius. This is the large, round, smooth region that faces medially.  The lateral aspect also contains multiple vascular foramina. The capitulum is a convex and rounded projection that covers the anterior and inferior surfaces of the lateral condyle of the humerus. Surgery can return the joint surface to its original smoothness, thus allowing for the return of normal function. On the posterior surface of the condyle is the olecranon fossa, which articulates with the olecranon of the ulnar bone upon flexion of the elbow joint. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the humerus - its bony landmarks and clinical correlations. Cross section views reveal it to be circular proximally and flattened distally. The medial epicondyle is a blunt projection superomedial to the medial condyle, which forms at the end of the medial border of the humerus. Both the greater and lesser tubercles serve as attachment sites for muscles that act across the shoulder joint. 2014 Aug;97 Suppl 8:S27-33. Ive been writing about ancient mixture between species for a long time now. The anterior interosseous nerve can be tested by asking the patient to make an okay sign, testing for weakness of flexor pollicis longus. The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the hand. It provides attachment for the last rotator cuff muscle - the subscapularis. The five metacarpal bones form the palm of the hand. The key neurovascular structures at risk here are the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex artery. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions. The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. Immediately distal to the supraepicondylar ridges areextracapsular projections of bone, the lateral andmedial epicondyles. If compression occurs, the resulting ischemia (lack of oxygen) due to reduced blood flow can quickly produce irreparable damage to the forearm muscles. Romer (1976) homologizes the capitellum in Archosauromorphs with the groove separating the medial and lateral condyles. It only has an anterior surface. Deep dissection. The radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm (see (Figure)). The trochlea has a surface shaped like a pulley and covers the anterior, posterior and inferior surfaces of the medial condyle of the humerus. The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones contribute to the formation of the radiocarpal joint. This allows it a freedom of motion that is independent of the other metacarpal bones, which is very important for thumb mobility. humeral head, The distal ends of the metacarpal bones articulate with the proximal phalanx bones of the thumb and fingers. The margin of the smooth area of the head is the anatomical neck of the humerus. The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm. The thumb contains a proximal and a distal phalanx, whereas the remaining digits each contain proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. This results in unopposed flexion of the wrist, known as wrist drop. The shaft of the humerus is the site of attachment for various muscles. An intertubercular groove appears proximally, which demarcates the two tubercles vertically. condyle humeral limb thoracic bones quizlet insertion This area contains the humerus. Bookshelf In addition, four major nerves for shoulder and upper limb muscles are closely associated with different regions of the humerus, and thus, humeral fractures may also damage these nerves. In the articulated hand, the carpal bones form a U-shaped grouping. The anatomical neck of the humerus is the residual epiphyseal plate. The following musclesattach to the humerus along its shaft: A mid-shaft fracture of the humerus risk damage to theradial nerve and profunda brachii artery (as they are tightly bound in the radial groove). Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site. Unlike the trochlea, it doesnt cover the posterior surface. Reading time: 13 minutes. The carrying angle is larger in females to accommodate their wider pelvis. Please use the, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance. This faces medially, upwards and backwards and is separated from the greater and lesser tuberosities by the anatomical neck. Both can be palpated at the elbow. This serves as an attachment point for a connective tissue structure that unites the distal ends of the ulna and radius. Legal. The deltoid muscle covers the lateral aspect of the greater tubercle, resulting in the normal rounded shape of the shoulder. -, Prescher A. Anatomical basics, variations, and degenerative changes of the shoulder joint and shoulder girdle. This involves a complete transverse fracture across the distal radius that drives the separated distal fragment of the radius posteriorly and superiorly. Due to the poor blood supply to the scaphoid bone, healing will be slow and there is the danger of bone necrosis and subsequent degenerative joint disease of the wrist. This results in separation of one or both of the condyles from the shaft of the humerus. The eight carpal bones form the base of the hand. These include the: The olecranon fossa is a deep hollowed area on the posterior surface, superior to the trochlea. The deltoid, corocobrachialis, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles attach to the anterior surface, with the triceps brachii attaching to the posterior. The most proximal portion of the humerus is the head of the humerus, which forms a ball and socket joint with the glenoid cavity on the scapula. The more medial of these areas is the trochlea, a spindle- or pulley-shaped region (trochlea = pulley), which articulates with the ulna bone. Romer, A.S. 1976 Osteology of the reptiles. Thus, it starts and finishes on the lateral side. The proximal and distal rows of carpal bones articulate with each other to form the midcarpal joint (see (Figure)). Fig 4 Bony landmarks of the distal humerus. The proximal humerus is marked by a head, anatomical neck, surgical neck, greater and lesser tuberosity and intertubercular sulcus. The proximal end of the humerus is dominated by a half-spherical articular surface, called the head, that forms the ball of the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. It articulates with the radius and ulna to form the elbow joint. It is more common in children than adults. Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Identify the divisions of the upper limb and describe the bones in each region, List the bones and bony landmarks that articulate at each joint of the upper limb, is found on the medial side of the forearm, has a head that articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, does not articulate with any of the carpal bones, has the radial tuberosity located near its distal end. The anterolateral surfaceis an area limited between the anterior and lateral borders. Here's an easy way to help you remember them! These spaces accommodate the forearm bones when the elbow is fully bent (flexed). The digits are also numbered 15, with the thumb being number 1. A direct blow to the arm can result in a transverse fracture of the humeral shaft. Between the two tubercles lies a deep grove called the intertubercular sulcus, through which the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii runs. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! Fig 3 Wristdrop of the left forearm, as a result of radial nerve palsy. By Anatomography [CC BY-SA 2.1 jp], via Wikimedia Commons, [caption id="attachment_8000" align="aligncenter" width="208"], [caption id="attachment_21152" align="aligncenter" width="871"], [caption id="attachment_10467" align="aligncenter" width="278"], [caption id="attachment_119738" align="aligncenter" width="658"], [caption id="attachment_3599" align="aligncenter" width="336"].
The lateral aspect also contains multiple vascular foramina. The capitulum is a convex and rounded projection that covers the anterior and inferior surfaces of the lateral condyle of the humerus. Surgery can return the joint surface to its original smoothness, thus allowing for the return of normal function. On the posterior surface of the condyle is the olecranon fossa, which articulates with the olecranon of the ulnar bone upon flexion of the elbow joint. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the humerus - its bony landmarks and clinical correlations. Cross section views reveal it to be circular proximally and flattened distally. The medial epicondyle is a blunt projection superomedial to the medial condyle, which forms at the end of the medial border of the humerus. Both the greater and lesser tubercles serve as attachment sites for muscles that act across the shoulder joint. 2014 Aug;97 Suppl 8:S27-33. Ive been writing about ancient mixture between species for a long time now. The anterior interosseous nerve can be tested by asking the patient to make an okay sign, testing for weakness of flexor pollicis longus. The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the hand. It provides attachment for the last rotator cuff muscle - the subscapularis. The five metacarpal bones form the palm of the hand. The key neurovascular structures at risk here are the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex artery. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions. The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. Immediately distal to the supraepicondylar ridges areextracapsular projections of bone, the lateral andmedial epicondyles. If compression occurs, the resulting ischemia (lack of oxygen) due to reduced blood flow can quickly produce irreparable damage to the forearm muscles. Romer (1976) homologizes the capitellum in Archosauromorphs with the groove separating the medial and lateral condyles. It only has an anterior surface. Deep dissection. The radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm (see (Figure)). The trochlea has a surface shaped like a pulley and covers the anterior, posterior and inferior surfaces of the medial condyle of the humerus. The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones contribute to the formation of the radiocarpal joint. This allows it a freedom of motion that is independent of the other metacarpal bones, which is very important for thumb mobility. humeral head, The distal ends of the metacarpal bones articulate with the proximal phalanx bones of the thumb and fingers. The margin of the smooth area of the head is the anatomical neck of the humerus. The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm. The thumb contains a proximal and a distal phalanx, whereas the remaining digits each contain proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. This results in unopposed flexion of the wrist, known as wrist drop. The shaft of the humerus is the site of attachment for various muscles. An intertubercular groove appears proximally, which demarcates the two tubercles vertically. condyle humeral limb thoracic bones quizlet insertion This area contains the humerus. Bookshelf In addition, four major nerves for shoulder and upper limb muscles are closely associated with different regions of the humerus, and thus, humeral fractures may also damage these nerves. In the articulated hand, the carpal bones form a U-shaped grouping. The anatomical neck of the humerus is the residual epiphyseal plate. The following musclesattach to the humerus along its shaft: A mid-shaft fracture of the humerus risk damage to theradial nerve and profunda brachii artery (as they are tightly bound in the radial groove). Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site. Unlike the trochlea, it doesnt cover the posterior surface. Reading time: 13 minutes. The carrying angle is larger in females to accommodate their wider pelvis. Please use the, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance. This faces medially, upwards and backwards and is separated from the greater and lesser tuberosities by the anatomical neck. Both can be palpated at the elbow. This serves as an attachment point for a connective tissue structure that unites the distal ends of the ulna and radius. Legal. The deltoid muscle covers the lateral aspect of the greater tubercle, resulting in the normal rounded shape of the shoulder. -, Prescher A. Anatomical basics, variations, and degenerative changes of the shoulder joint and shoulder girdle. This involves a complete transverse fracture across the distal radius that drives the separated distal fragment of the radius posteriorly and superiorly. Due to the poor blood supply to the scaphoid bone, healing will be slow and there is the danger of bone necrosis and subsequent degenerative joint disease of the wrist. This results in separation of one or both of the condyles from the shaft of the humerus. The eight carpal bones form the base of the hand. These include the: The olecranon fossa is a deep hollowed area on the posterior surface, superior to the trochlea. The deltoid, corocobrachialis, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles attach to the anterior surface, with the triceps brachii attaching to the posterior. The most proximal portion of the humerus is the head of the humerus, which forms a ball and socket joint with the glenoid cavity on the scapula. The more medial of these areas is the trochlea, a spindle- or pulley-shaped region (trochlea = pulley), which articulates with the ulna bone. Romer, A.S. 1976 Osteology of the reptiles. Thus, it starts and finishes on the lateral side. The proximal and distal rows of carpal bones articulate with each other to form the midcarpal joint (see (Figure)). Fig 4 Bony landmarks of the distal humerus. The proximal humerus is marked by a head, anatomical neck, surgical neck, greater and lesser tuberosity and intertubercular sulcus. The proximal end of the humerus is dominated by a half-spherical articular surface, called the head, that forms the ball of the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. It articulates with the radius and ulna to form the elbow joint. It is more common in children than adults. Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Identify the divisions of the upper limb and describe the bones in each region, List the bones and bony landmarks that articulate at each joint of the upper limb, is found on the medial side of the forearm, has a head that articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, does not articulate with any of the carpal bones, has the radial tuberosity located near its distal end. The anterolateral surfaceis an area limited between the anterior and lateral borders. Here's an easy way to help you remember them! These spaces accommodate the forearm bones when the elbow is fully bent (flexed). The digits are also numbered 15, with the thumb being number 1. A direct blow to the arm can result in a transverse fracture of the humeral shaft. Between the two tubercles lies a deep grove called the intertubercular sulcus, through which the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii runs. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! Fig 3 Wristdrop of the left forearm, as a result of radial nerve palsy. By Anatomography [CC BY-SA 2.1 jp], via Wikimedia Commons, [caption id="attachment_8000" align="aligncenter" width="208"], [caption id="attachment_21152" align="aligncenter" width="871"], [caption id="attachment_10467" align="aligncenter" width="278"], [caption id="attachment_119738" align="aligncenter" width="658"], [caption id="attachment_3599" align="aligncenter" width="336"].